
Environmental impacts of economic development | Geography Revision - Source geography-revision.co.uk
In this guide, we will explore the environmental impacts, economic consequences, and ethical implications of a cotton ban. We will also provide some key takeaways that can help you make informed decisions about your clothing choices.
| Cotton | Alternative Materials | |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | High water usage, pesticide use, and greenhouse gas emissions | Lower water usage, reduced pesticide use, and lower greenhouse gas emissions |
| Economic Consequences | Job losses in the cotton industry | Job creation in the alternative materials industry |
| Ethical Implications | Pesticide exposure and hazardous working conditions for cotton farmers | Improved working conditions for farmers and reduced pesticide exposure |
- Environmental Impacts of Cotton Production
- Economic Consequences of a Cotton Ban
- Ethical Implications of a Cotton Ban
- Key Takeaways
FAQ
This FAQ section addresses frequently asked questions and misconceptions surrounding the environmental impacts, economic consequences, and ethical implications of the cotton ban.
Question 1: What are the primary environmental impacts of cotton production?
Cotton farming consumes substantial amounts of water, pesticides, and fertilizers, leading to water depletion, soil degradation, and pollution. Furthermore, the use of genetically modified cotton strains raises concerns about biodiversity loss and potential health risks.
Question 2: How does a cotton ban affect the economic livelihoods of cotton farmers and industry workers?
A cotton ban would undoubtedly have economic consequences for farmers and workers dependent on the industry. It could lead to job losses, reduced incomes, and economic hardship in cotton-producing regions. The transition to alternative crops or sustainable farming practices would require significant support and investment.
Question 3: Are there viable alternative fibers to cotton that can meet global demand?
Several alternative fibers, such as hemp, bamboo, and organic cotton, offer sustainable and eco-friendly options. However, scaling up production to meet the global demand for cotton would require significant investment, research, and collaboration.
Question 4: What are the ethical considerations associated with the cotton industry?
The cotton industry has a history of labor exploitation, particularly in developing countries. A cotton ban could potentially address these ethical concerns by promoting fair labor practices and ensuring that workers' rights are respected throughout the supply chain.
Question 5: Can a cotton ban effectively address the environmental and ethical issues associated with its production?
While a cotton ban may not be the sole solution to the complex issues surrounding cotton production, it can serve as a catalyst for change. It could encourage innovation, promote sustainable practices, and stimulate the development of alternative fibers. However, a comprehensive approach involving all stakeholders, including governments, industries, and consumers, is crucial for lasting impact.
Question 6: What steps can consumers take to support sustainable cotton practices?
Consumers play a vital role in driving change through their purchasing choices. Opting for certified organic cotton, recycled cotton, or alternative fibers supports sustainable farming and ethical practices. Additionally, advocating for transparency and traceability in the supply chain ensures that consumers can make informed decisions.
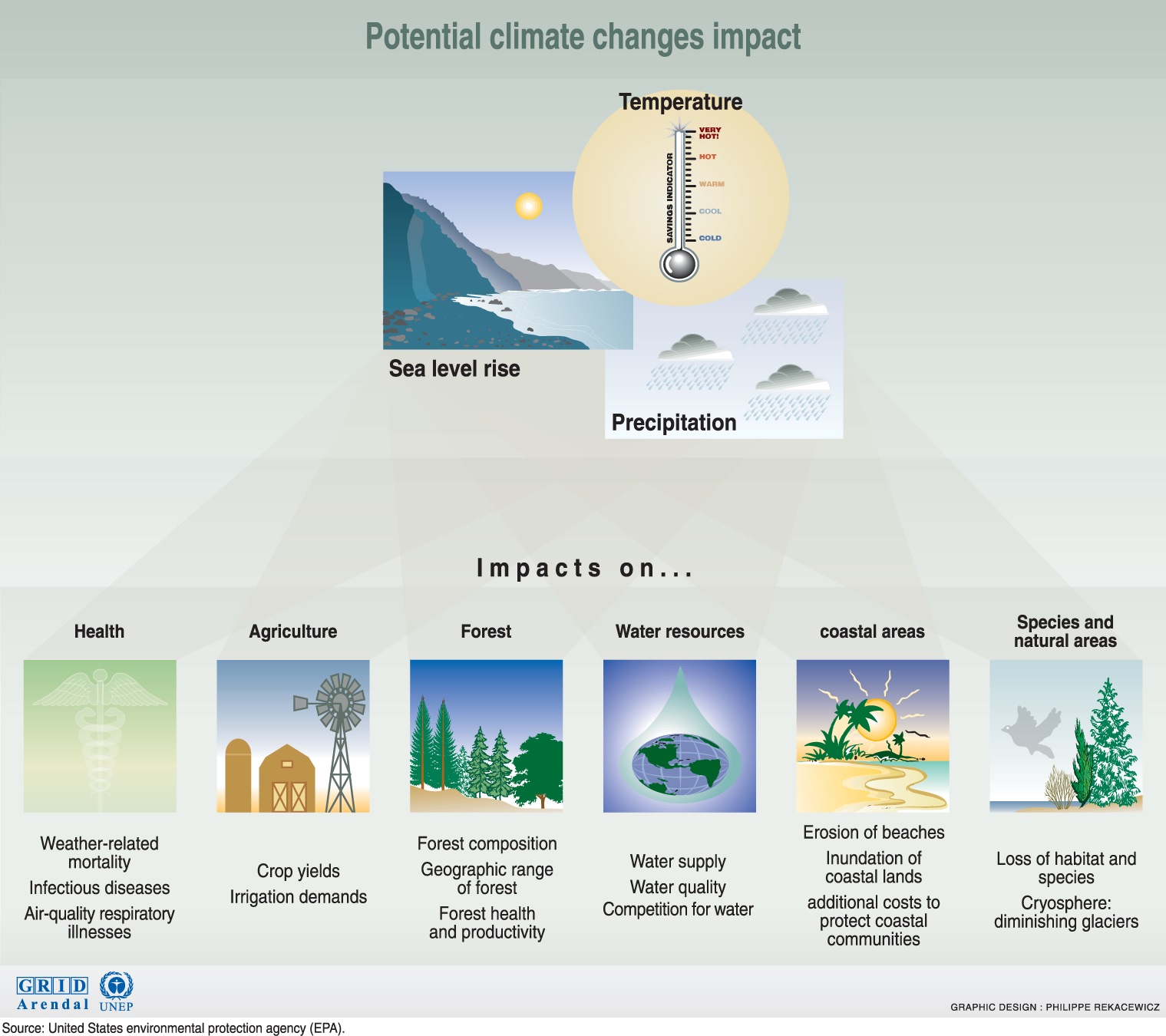
Climate Change: Consequences and Repercussions — Beyond Weather & The - Source beyondweather.ehe.osu.edu
The key takeaway is that a cotton ban, while not a simple solution, can initiate a dialogue about the environmental, economic, and ethical concerns associated with cotton production. It can foster a transition towards sustainable practices, support alternative fibers, and promote ethical considerations throughout the supply chain.
The next article section will delve deeper into the specific consequences of a cotton ban on the global economy.
Tips to Understand Cotton Ban's Impacts
The Cotton Ban: Environmental Impacts, Economic Consequences, And Ethical Implications highlights the need to understand the complex impacts of banning cotton production. Here are some key tips to grasp the significance of this issue:
Tip 1: Assess Environmental Impacts:
Recognize the severe environmental consequences, including soil degradation, water scarcity, and chemical pollution associated with conventional cotton farming. Explore alternative cultivation practices and sustainable supply chains to mitigate these detrimental effects.
Tip 2: Consider Economic Consequences:
Analyze the economic implications, particularly in cotton-producing regions where livelihoods and industries rely heavily on this crop. Evaluate job losses, market fluctuations, and alternative economic opportunities to ensure a balanced approach.
Tip 3: Examine Ethical implications:
Address the ethical concerns surrounding labor practices, particularly in developing countries where child labor and poor working conditions may be prevalent. Promote fair trade practices, worker empowerment, and sustainable agriculture to uphold ethical standards.
Tip 4: Explore Alternative Materials:
Investigate eco-friendly alternatives to cotton, such as organic cotton, hemp, or bamboo. Support research into innovative materials that reduce environmental impact and promote social responsibility.
Tip 5: Engage with Stakeholders:
Facilitate dialogue among all stakeholders, including farmers, manufacturers, consumers, and policymakers. Encourage collaboration and knowledge sharing to ensure informed decision-making.
Tip 6: Support Research and Innovation:
Promote ongoing research to develop sustainable cotton farming techniques, alternative materials, and innovative processing methods. Support initiatives that drive technological advancements to address the challenges faced by the cotton industry.
Tip 7: Educate Consumers:
Raise awareness about the impacts of conventional cotton production and the ethical implications associated with it. Encourage consumers to make informed choices, support sustainable practices, and advocate for change.
Conclusion:
By considering these tips, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted impacts of cotton bans. Collaborative efforts, informed decision-making, and a commitment to sustainability are crucial for shaping a more equitable and environmentally conscious future.
Cotton Ban: Environmental Impacts, Economic Consequences, And Ethical Implications
The ban on cotton cultivation poses environmental, economic, and ethical implications that require careful examination.
- Water Conservation
- Soil Degradation Reduction
- Biodiversity Preservation
- Economic Dependency
- Livelihood Disruption
- Fairness and Equity
The environmental benefits of a cotton ban are undeniable. Cotton cultivation is a water-intensive process, and reducing its production can help conserve precious water resources. Additionally, it can prevent soil degradation and erosion, and promote biodiversity by reducing the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers. However, the economic consequences of a cotton ban are also significant. Many farmers rely on cotton as their primary source of income, and a ban could lead to widespread economic hardship. Furthermore, the ban could have ethical implications, as it may unfairly burden those who depend on cotton for their livelihoods.

Climate change impacts | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration - Source www.noaa.gov
Cotton Ban: Environmental Impacts, Economic Consequences, And Ethical Implications
The cultivation and production of cotton has a significant environmental impact, economic consequences, and ethical implications. Understanding the connections between these factors is crucial for informed decision-making and sustainable cotton practices.

Disposal of E-Waste: How Electronic Waste Impacts The Environment - Source www.rakicomp.com
Environmentally, cotton farming consumes vast amounts of water and chemicals, contributing to water scarcity and pollution. The use of pesticides and herbicides can harm ecosystems and biodiversity. Economically, cotton production is a major source of income for many countries, but it also faces challenges such as fluctuating prices, labor exploitation, and unfair trade practices. Ethically, cotton production raises concerns about human rights violations, child labor, and the displacement of indigenous communities.
Addressing these interconnected issues requires a holistic approach that considers the environmental, economic, and ethical dimensions. Sustainable cotton practices, such as organic farming, fair trade initiatives, and responsible water management, aim to mitigate negative impacts and promote social equity. Collaborative efforts between governments, industries, and consumers are essential to create a sustainable cotton sector that balances environmental protection, economic viability, and ethical considerations.
Conclusion
Exploring "Cotton Ban: Environmental Impacts, Economic Consequences, And Ethical Implications" highlights the complex interconnections between these factors. Sustainable cotton practices are essential to address environmental degradation, economic disparities, and ethical concerns. By embracing holistic approaches and fostering collaboration, we can create a cotton industry that meets the needs of both people and the planet.
The future of cotton production lies in responsible and sustainable practices that prioritize environmental conservation, economic equity, and social justice.